site_4bbb466c-cafd-4edb-8869-71ed8e60d33a
Excellence in PGR technology
Gibberellic Acid for Plants Top Tips for Optimal Growth?
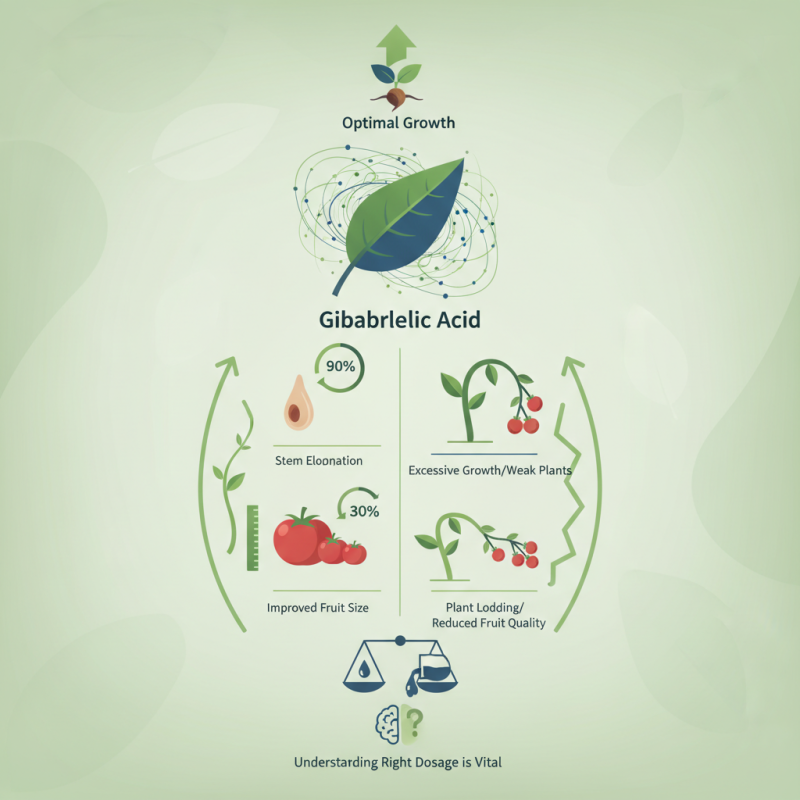
Gibberellic acid for plants is a powerful growth regulator. It plays a crucial role in enhancing plant development. Studies show that it can increase seed germination rates by up to 90%. This can significantly impact crop yield.
In agriculture, gibberellic acid stimulates stem elongation and improves fruit size. Research from the American Society of Horticultural Science found that treatments with gibberellic acid resulted in a 30% increase in tomato yield. However, there are risks involved. Overuse can lead to excessive growth and weaker plants.
Farmers should carefully balance gibberellic acid applications. Too much can cause problems like plant lodging or reduced fruit quality. Understanding the right dosage is vital for optimal results. These insights underscore the importance of thoughtful use of gibberellic acid in cultivation practices.
Understanding Gibberellic Acid and Its Role in Plant Growth
Gibberellic acid is a plant hormone that plays a crucial role in growth and development. It is involved in various processes, such as seed germination, flowering, and fruit development. By promoting cell elongation, gibberellic acid helps plants grow taller and healthier. Its influence on plant growth cannot be overstated.
Using gibberellic acid can lead to impressive results. For example, it can enhance seedling vigor, making the plants more robust. However, it requires careful application. Too much might cause stunted growth or abnormal shapes. Observing the plants closely allows gardeners to learn the right concentration needed. Mistakes happen; it's part of the process.
Understanding how plants respond to gibberellic acid takes time. Each species reacts differently, which can be frustrating. Some may require more hormone, while others do better with less. Keeping a growth journal can help track these variables. Observations lead to better decisions in future applications. Each experience adds to knowledge, shaping a fruitful gardening journey.
Effects of Gibberellic Acid on Plant Height Growth
This chart illustrates the impact of different concentrations of Gibberellic Acid (GA₃) on the average height of plants. As the concentration of GA₃ increases, there is a noticeable improvement in plant height, demonstrating its positive role in promoting growth.
Benefits of Gibberellic Acid for Different Plant Species
Gibberellic acid (GA) is a plant hormone that promotes growth. It is particularly effective in various plant species. Studies show that GA enhances seed germination. In rice and barley, GA-treated seeds sprout faster by 25%. This rapid germination can lead to earlier harvests.
Different plant species react differently to gibberellic acid. For example, in grapes, GA increases berry size and improves yield by up to 30%. However, not all plants benefit equally. Some crops may require different concentrations to avoid negative effects. Excess GA can lead to weak stems.
For leafy vegetables like lettuce, GA promotes elongation. Gardeners can use it to achieve tender greens. Results can vary based on environmental conditions. While GA's benefits are clear, it is essential to monitor plants closely. Overuse can distort growth patterns or reduce quality. Each plant species necessitates tailored applications for the best results.
Application Methods for Gibberellic Acid in Horticulture
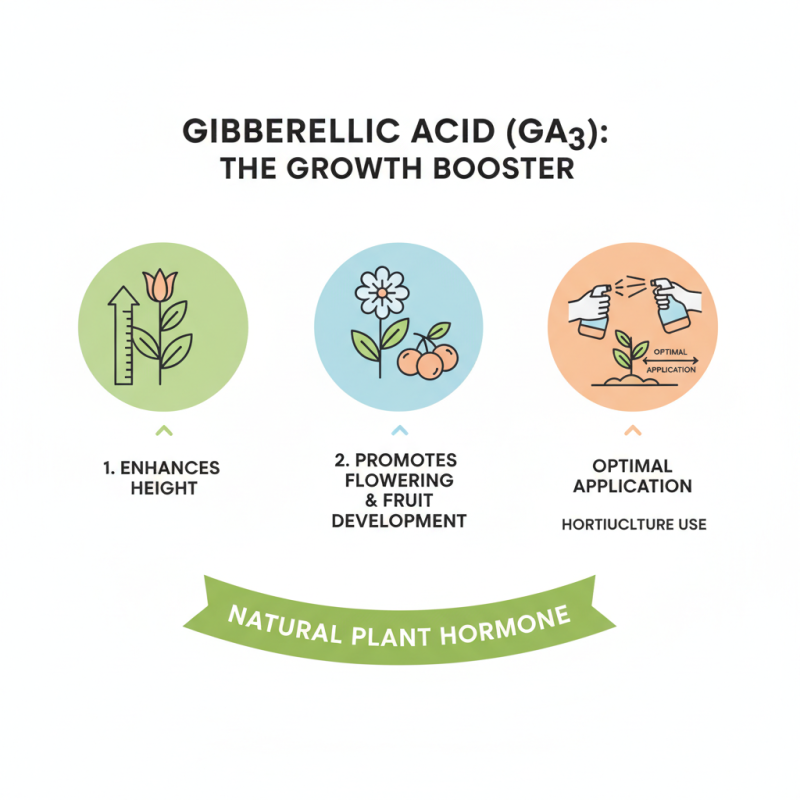
Gibberellic acid (GA3) is a naturally occurring plant hormone that promotes growth. Its application can significantly enhance plant height, flowering, and fruit development. In horticulture, proper application methods are essential for maximizing the benefits of GA3.
One effective method is foliar spraying. This involves dissolving GA3 in water and spraying it directly onto the leaves. Research shows that foliar application can lead to a 30% increase in plant height in certain species. Timing is crucial; applying GA3 during active growth periods can yield better results.
Soil application is another approach. This method allows the roots to absorb the hormone directly. Studies indicate that soil applications can enhance germination rates by up to 40%. However, over-application can harm plant health. Always follow recommended dosages.
When using gibberellic acid, it’s essential to monitor the plants closely. Look for signs of stress or overgrowth. Adjust application methods based on plant response. Proper observation leads to better results. Growers should experiment with different concentrations to find what works best for their specific crops.
Optimal Concentrations and Timing for Gibberellic Acid Use
Gibberellic acid (GA3) is a powerful plant growth regulator. Its effectiveness largely depends on concentration and timing. Studies suggest that concentrations between 50 to 200 ppm can significantly enhance growth in various crops. For instance, in corn, applying GA3 at 100 ppm increased height by 15%. The timing of application also plays a crucial role. Early application during seedling stages often results in better results.
For optimal results, it's essential to consider environmental factors. Temperature, humidity, and plant species all influence GA3's effectiveness. Some reports indicate that too much gibberellic acid can lead to weaker plants and delayed maturity. Over-application risks creating imbalances in nutrient absorption. Understanding the specific needs of each plant species helps prevent such issues.
Farmers and growers should conduct small trials before large-scale applications. Monitoring plant responses can provide valuable insights. Each crop responds differently to GA3. Continuous research is necessary to refine application techniques. Adapting to each situation will lead to healthier plants and better yields.
Potential Risks and Considerations When Using Gibberellic Acid
When using gibberellic acid in horticulture, caution is essential. This plant hormone can promote rapid growth and improve yields. However, overuse may lead to undesirable effects. For instance, excessive application can make plants leggy and weak. They may lose their natural resistance to diseases. A delicate balance is necessary.
Understanding the right dosage is critical. Too little may not produce results, while too much can harm your plants. It's wise to start small and observe how your plants react. Some plants might show sensitivity to gibberellic acid. Signs of stress can appear, like yellowing leaves or stunted growth. Regular monitoring is key.
Additionally, timing plays a vital role in the application process. Using it at the wrong phase can disrupt normal growth patterns. It’s important to adapt your approach depending on the plant species. Not all plants respond the same way. This trial and error can lead to insights, but be prepared for setbacks. A thoughtful strategy will yield the best outcomes in plant health and productivity.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Gibberellic Acid Uses in Plants You Should Know?
-

2026 How to Effectively Use Gibberellic Acid for Plant Growth?
-

What is Gibberellic Acid and How Does it Affect Plant Growth?
-
Understanding Gibberellic Acid Label: Uses, Benefits, and Safety Information
-

How to Effectively Use Gibberellic Acid Products for Plant Growth?
-

What is Gibberellic Acid and How to Use Gibberellic Acid Products Effectively
